Cache Is a Separate Chip That Takes Longer to Access
Clock speed is measured in trillions of cycles per hour. But Jigsaw didnt build cache hierarchies which makes the allocation problem much more.
What Is A Cache A Complete Guide To Caches And Their Uses
The data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere.
. Longer cache lines expand spatial locality by holding values from more adjacent addresses. Imagine having only one cache line even if a program has high temporal locality if there is one other. The QWERTY keyboard was developed in _____.
Has a storage capacity of. _____ connects a computer to a telephone line for dial-up. A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit CPU of a computer to reduce the average cost time or energy to access data from the main memory.
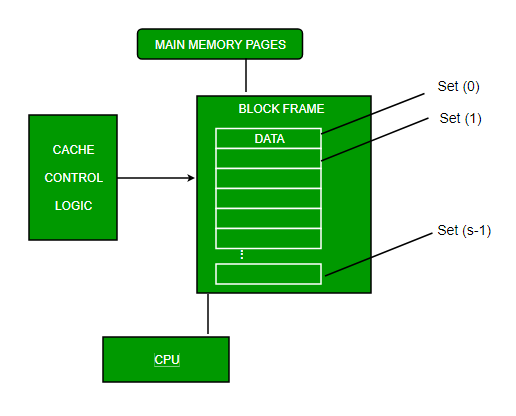
Cache memory is used to reduce the average time to access data from the Main memory. There are fewer cache lines but they are longer. This cache memory is mainly divided into 3 levels as Level 1 Level 2 and Level 3 cache memory but sometimes it is also said that there is 4 levels cache.
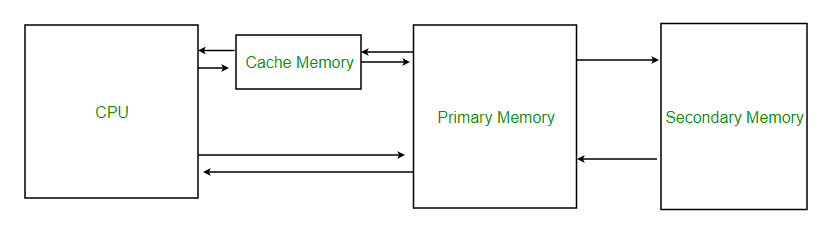
Also known as the processor. L2 and L3 caches are bigger than L1. In computing a cache is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster.
The most common personal printers. L2 and L3 caches are larger than L1 but take longer to access. Cache memory is sometimes called CPU central processing unit memory because it is typically integrated directly into the CPU chip or placed on a separate chip that has a separate bus interconnect with the CPU.
Its size is often restricted to between 8 KB and 64 KB. A memory cache sometimes called a cache store a memory buffer or a RAM cache is a portion of memory made up of high-speed static RAM SRAM instead of the slower and cheaper dynamic RAM DRAM. Base machine with CPI 10 if all references hit the L1 2 GHz Main.
Examples of L1 cache are accumulator Program counter and address register etc. A cache pronounced cash is an intermediate storage that retains data for repeat access. Cache is commonly used by the central.
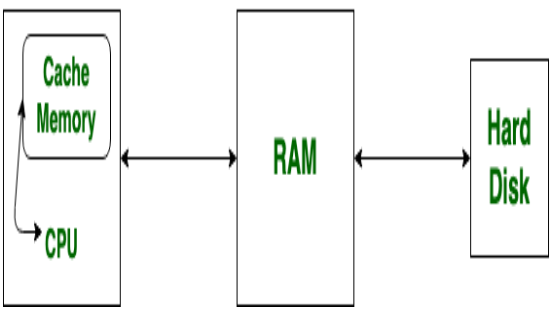
Memory caching is effective because most programs access the same instructions over and over. The CPU cache is a very small memory module mounted on the CPU chip which stores files that are frequently used to operate different applications. Therefore it is more accessible to the processor and able to increase efficiency because its physically close to the processor.
In multi-core CPUs a separate L1 cache is available for each core. The _____ cache is a separate chip that takes longer to access. For each core Jenga knows how long it would take to retrieve information from any on-chip memory bank a measure known as latency Jenga builds on an earlier system from Sanchezs group called Jigsaw which also allocated cache access on the fly.
Level 2 L2 cache or Secondary Cache There are also L2 caches for larger processors but take longer to access. The main circuit board of a computer. L2 caches are less expensive and larger than L1 caches so L2 cache sizes tend to be larger and may be of the order of 256 KB per core.
Multi-core CPUs will generally have a separate L1 cache for each core. Its actually a very fast type of random-access memory. Introduction to Cache Memory Types.
Its architecture allows the processor to access information stored in the cache memory module at ultra-fast transfer speeds. The cost of this memory is higher than the main memory of the computer as well as external hard disks. Instead of just having an on-chip L1 cache an off-chip L2 cache is helpful Ex.
The cache is a smaller and faster memory which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. In the below section let us see each level of cache memory in detail. L1 is usually part of the CPU chip itself and is both the smallest and the fastest to access.
A multi-core processor consists of two or more processors that are integrated on a single chip. L2 cache may also be located in the CPU chip although not as close to the core as L1 cache. Cached data is stored temporarily in an accessible storage media thats local to the cache client and separate from the main storage.
Caches represent a transparent layer between the user and the actual source of the data. Cache hits are served. A cache is a smaller faster memory located closer to a processor core which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations.
It reduces the time needed to access the data again. A separate chip that takes longer to access. Level 1 cache is also known as registers which are a type of memory that is embedded in the processor.
Generally the L1 cache is the smallest in size and built into the processor chip. There are various different independent caches in a CPU which store instructions and data. The process for saving data in a cache is called caching.
Fewer cache lines can lead to more con ict misses so the window for temporal locality is worse. Or more rarely it may be located on a separate chip close to the CPU. Cache is the temporary memory officially termed CPU cache memory This chip-based feature of your computer lets you access some information more quickly than if you access it from your computers main hard drive.
A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Going back in time to the days of the original Intel Pentium Level 2 cache was a separate chip either on a small plug-in circuit board like a. In Cache Memory Types Cache Memory is a high-speed auxiliary memory that holds frequently accessed instructions and data to make it available to the processor at the shortest possible time thus reducing the overall process cycle time.

Cache Memory In Computer Organization Geeksforgeeks

No comments for "Cache Is a Separate Chip That Takes Longer to Access"
Post a Comment